The Household versus natural environment SAILS unit focuses on the environmental implications of the use of cleaning agents. Students investigate the growth of cress in various conditions, allowing them to determine the impact of commonly used household chemicals on the environment. Students assess the consequences of daily decisions taken in their homes and thus develop a sense of responsibility for the actions they take. This unit is recommended for implementation at both lower and upper second level, as a guided or open inquiry conducted over two lesson periods.
This unit can be used for development of many inquiry skills, in particular planning investigations, developing hypotheses and working collaboratively. In addition, students can develop their scientific reasoning skills through collecting data and drawing conclusions, and enrich their scientific literacy by critically evaluating their investigations. Some assessment methods described include teacher observation, use of student artefacts and self-assessment.
This unit was trialled in Ireland, Greece, Portugal and Poland – producing six case studies of implementation (lower and upper second level students; mixed ability and gender). Key skills assessed were planning investigations, working collaboratively and forming coherent arguments. This activity was shown to enrich students' scientific literacy, in particular the ability to present scientific data and to understand the environment impact of household chemicals. Assessment was based on teacher observation and the evaluation of students' presentations.
- Properties of cleaning and washing agents
- Ecotoxicity
- Lower
- Upper
- Planning investigations
- Developing hypotheses
- Forming coherent arguments
- Working collaboratively
- Scientific reasoning
- Scientific literacy
- Classroom dialogue
- Teacher observation
- Peer-assessment
- Self-assessment
- Worksheets
- Student devised materials
- Presentations
- Other assessment items
The teaching and learning activities described in the Household versus natural environment SAILS inquiry and assessment unit were based on the “Sustainable washing for a clean environment” project, which was further developed by the FP7 ESTABLISH project unit Chemical care. The activity was adapted for the SAILS project by the team at Jagiellonian University.
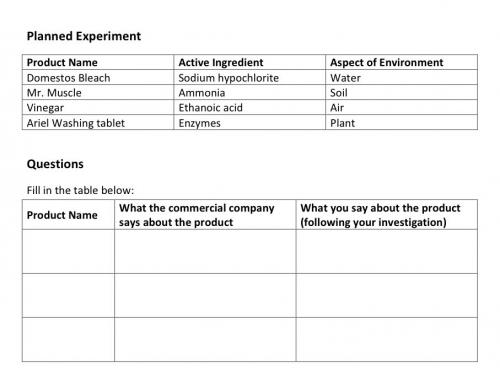
The problem under consideration in this unit is the ecological consequences of the use of cleaning agents at home (e.g. detergents used to clean textiles). The outlined investigation allows students to assess the consequences of everyday decisions in a scientific way. The aim is to give 14 to 18-year-old students an insight into the potential environmental effects of the incorrect use of household chemicals, such as detergents. Various household detergents may be the subject of investigation, which will allow the teacher to match the activities to the students’ interests. In addition, the proposed activity may be implemented as a guided or open inquiry, as appropriate for the student group.
In this section we present some tools for formative assessment of the following competencies: students’ prior knowledge, involvement in the discussion, inquiry plans, data presentation, ability to search for information and group work. Several key opportunities have been identified for the assessment of inquiry skills during this activity, and tools for the assessment include observation sheets, rubrics and self-assessment cards. It is recommended that the teacher pre-select some students for evaluation through in-class observation, while all students can be assessed through collection of student artefacts, such as group worksheets.
Below you can find the full inquiry and assessment unit for download, as well as an archive with classroom materials, including student worksheets and assessment tools for teachers to be used during the activities if available.
Unit booklet Classroom materials| Concept focus |
Properties of household cleaning and washing agents
Ecotoxicity
|
| Inquiry skills focus |
Planning investigations
Developing hypotheses
Working collaboratively
|
| Scientific reasoning |
Considering the influence of various factors
|
| Scientific literacy |
Drawing conclusions using reasoned arguments and evidence
Presenting scientific results
|
| Assessment methods |
Classroom dialogue
Teacher observation
Worksheets
Student devised materials
Presentations
|
This unit was trialled in four countries, producing six case studies of its implementation – CS1 Ireland, CS2 Greece, CS3 Portugal and CS4-CS6 Poland. In all case studies, the students involved had little or limited experience of inquiry learning and only in CS1 Ireland had the teacher significant experience in IBSE. The teachers used a guided inquiry teaching approach, which included the provision of student worksheets and specific guiding questions.
The unit is recommended for students aged 14-18 years, and was implemented with lower second level classes in CS1 Ireland, CS2 Greece and CS3 Portugal and at upper second level in the Polish case studies (CS4-6) and one class in CS1 Ireland. The students worked in smaller groups, usually of 3-5 students. The groups were mostly formed independently by the students, but in CS4 Poland student-groups were assigned by the teacher. Students in most classes were of mixed gender and ability, although in CS1 Ireland the class was all female.
The case studies identify the versatility of the unit in that it allowed teachers to focus on different concepts and inquiry skills to be developed and assessed. It can be used at different levels, as shown in the case studies where it was used with lower and upper second level students. Finally, the case studies demonstrate a range of strategies and assessment data that can be collected to assess student inquiry development.
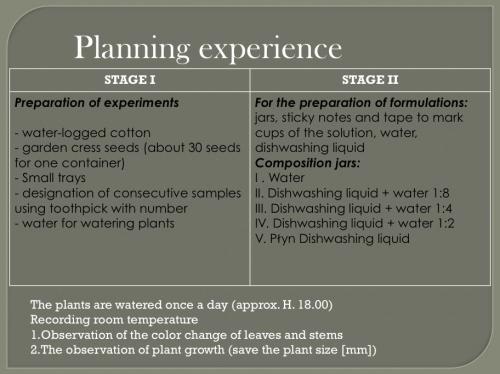
Since most students had not conducted studies in the IBSE strategy before, the teachers chose to use a guided inquiry teaching approach. Several of the teachers developed worksheets, which were provided to the students to guide their work (CS1 Ireland, CS2 Greece, CS3 Portugal and CS6 Poland). There was some variation in the level of openness of the guided approaches used at various stages in the activities. In all case studies, examples of students being led by multiple teacher questions are evident.
There were variations in how the unit was delivered in the different countries. In all case studies, whole-class discussions were used, but the majority of the activity was carried out in smaller groups. The group sizes ranged from pairs to groups of five. In general, groups were of mixed gender, although CS1 Ireland details implementation in a single sex school (all-girls) and CS3 Portugal observes that one single-sex grouping was formed in addition to a mixed gender group.
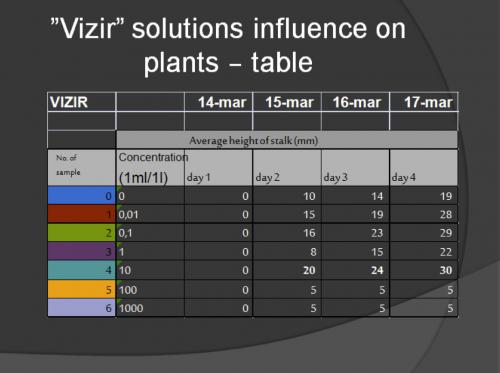
Within the six case studies, the teachers used a variety of formative and summative assessment strategies; these included teacher observation, teacher questioning, student self-assessment and analysis of student work. The following competences were evaluated: students’ prior knowledge, involvement in the discussion, planning investigations, data presentation, skill in searching for information and group work. Teacher and student rubrics were used in many of the case studies to help the teachers to make judgements on student work and for the students to assess their own development. Whilst students gained experience of many inquiry skills not all of these were assessed. Developing hypotheses, forming coherent arguments and planning investigations were each assessed in three of the six case studies, while several case studies describe evaluation of scientific reasoning capabilities and scientific literacy (CS1 Ireland, CS4-6 Poland).
Below you can find the full inquiry and assessment unit for download (excluding the case studies), as well as an archive containing all the case studies.
Unit booklet Case studies| Concept focus |
Environmental impact of household chemicals
|
| Activities implemented |
Household versus natural environment
|
| Inquiry skills assessed |
Developing hypotheses
|
| Scientific reasoning |
Identifying variables
|
| Assessment methods |
Classroom dialogue
Teacher observation
Worksheets
|
| Level |
Lower
Upper
|
| Age |
13-16
|
| Prior experience with inquiry |
No experience
|
| Concept focus |
Environmental impact of household chemicals
|
| Activities implemented |
Household versus natural environment
|
| Inquiry skills assessed |
Planning investigations
Forming coherent arguments
|
| Assessment methods |
Classroom dialogue
Teacher observation
Peer-assessment
Worksheets
Presentations
|
| Level |
Lower
|
| Age |
13-14
|
| Prior experience with inquiry |
No experience
|
| Concept focus |
Environmental impact of household cleaners
|
| Activities implemented |
Household versus natural environment
|
| Inquiry skills assessed |
Developing hypotheses
Working collaboratively
|
| Assessment methods |
Classroom dialogue
Teacher observation
Self-assessment
Worksheets
Student devised materials
|
| Level |
Lower
|
| Age |
13-16
|
| Prior experience with inquiry |
No experience
|
| Concept focus |
Environmental impact of household chemicals
|
| Activities implemented |
Household versus natural environment
|
| Inquiry skills assessed |
Developing hypotheses
Working collaboratively
|
| Scientific literacy |
Searching for information
Presentation of scientific results
|
| Assessment methods |
Classroom dialogue
Teacher observation
Self-assessment
Student devised materials
Presentations
|
| Level |
Upper
|
| Age |
17
|
| Prior experience with inquiry |
No experience
|
| Concept focus |
Environmental impact of household chemicals
|
| Activities implemented |
Household versus natural environment
|
| Inquiry skills assessed |
Planning investigations
Forming coherent arguments
|
| Scientific literacy |
Searching for information
Presentation of scientific results
|
| Assessment methods |
Classroom dialogue
Teacher observation
Student devised materials
Presentations
|
| Level |
Upper
|
| Age |
16-17
|
| Prior experience with inquiry |
No experience
|
| Concept focus |
Environmental impact of household chemicals
|
| Activities implemented |
Household versus natural environment
|
| Inquiry skills assessed |
Planning investigations
Forming coherent arguments
|
| Scientific reasoning |
Data entry and observation skills
|
| Scientific literacy |
Presentation of scientific data
|
| Assessment methods |
Classroom dialogue
Teacher observation
Worksheets
Student devised materials
Presentations
Other assessment items
|
| Level |
Upper
|
| Age |
17
|
| Prior experience with inquiry |
No experience
|